Configure Linux Services (systemd, systemctl)
Fedora 15 introduced
systemd as a replacement for the previous sysvinit service management. Since RHEL7 and Oracle Linux 7 are based on Fedora 19, the switch from sysvinit to systemd is now part of the Enterprise Linux distributions. This article is a rework of the previous Linux Service article, bringing it up to date.Backwards Compatibility
The transition to using
systemd is made easier by the fact the service and chkconfig commands are still available. They have been reworked to call the equivalent systemctl commands. What's more, they sometimes output the command they are redirecting too, making learning the new systemd commands much easier.# service nfs restart Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart nfs.service #
On Fedora, this backwards compatibility also extends to the
system-config-services tool, which is still available. This package is not available in the RHEL7/OL7 distributions.Starting and Stopping Services
When using
sysvint these actions were achieved using the service command, with the service definitions located in the "/etc/init.d" directory. Under systemd, the service definitions are located in the "/lib/systemd/system/" directory.# ls /lib/systemd/system/httpd.service /lib/systemd/system/httpd.service #
The
systemctl command is used to stop, start, restart and check the status of a specified service. Unlike the service command, most systemctl commands do not produce any status output on the command line. Services can be referenced with or without the ".service" suffix.# systemctl stop httpd # systemctl stop httpd.service # systemctl start httpd # systemctl start httpd.service # systemctl restart httpd # systemctl restart httpd.service # systemctl status httpd # systemctl status httpd.service
The output from the
systemctl status command is quite different to that of the service command.# systemctl status httpd
httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2014-04-20 09:26:18 BST; 32min ago
Main PID: 16314 (httpd)
Status: "Total requests: 0; Current requests/sec: 0; Current traffic: 0 B/sec"
CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service
├─16314 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─16315 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─16316 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─16317 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─16318 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
└─16319 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
Apr 20 09:26:18 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Se...
Apr 20 09:26:18 localhost.localdomain httpd[16314]: AH00558: httpd: Could not...
Apr 20 09:26:18 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Ser...
Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
#
Use the following commands to get the status of all services.
# # All loaded and active services. # systemctl list-units --type service # # All loaded services # systemctl list-units --type service --all # # All available services # systemctl list-unit-files --type service
Enabling and Disabling Services
Under
sysvint the chkconfig command was used to perform these actions. Under systemd the systemctl command is used to enable and disable services to auto-start at reboot.# systemctl enable httpd ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service' # # systemctl disable httpd rm '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service' #
system-config-services
On Fedora the "Service Configuration" dialog is available from the menu (System > Administration > Services) or directly from the command line by running the
system-config-servicescommand.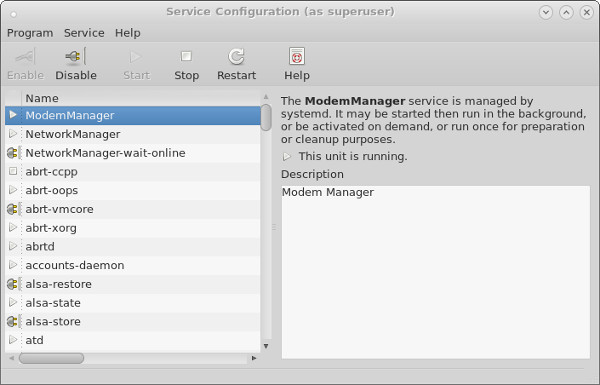
The "Enable" and "Disable" buttons are used to toggle the auto-start on reboot for each service. The "Start", "Stop" and "Restart" buttons affect the current state of the service.
Creating Linux Services
As an example, in this section we will create a new service to automatically start/stop an Oracle database. This assumes the Oracle database is not using Oracle Restart and the "start_all.sh" and "stop_all.sh" scripts are already present, as described here.
Create the service file called "/lib/systemd/system/dbora.service".
[Unit] Description=The Oracle Database Service After=syslog.target network.target [Service] # systemd ignores PAM limits, so set any necessary limits in the service. # Not really a bug, but a feature. # https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=754285 LimitMEMLOCK=infinity LimitNOFILE=65535 #Type=simple # idle: similar to simple, the actual execution of the service binary is delayed # until all jobs are finished, which avoids mixing the status output with shell output of services. RemainAfterExit=yes User=oracle Group=oinstall ExecStart=/home/oracle/scripts/start_all.sh ExecStop=/home/oracle/scripts/stop_all.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Thanks to Javier and Mark in the comments for their suggestions about using
RemainAfterExit, User and Group in this file.
If you are using NFS storage, you need to define the dependency between Oracle and NFS.
[Unit] Description=The Oracle Database Service Requires=rpc-statd.service network.target nfs.service nfs-mountd.service local-fs.target remote-fs.target After=syslog.target network.target nfs.service nfs-mountd.service local-fs.target rpc-statd.service remote-fs.target [Service] # systemd ignores PAM limits, so set any necessary limits in the service. # Not really a bug, but a feature. # https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=754285 LimitMEMLOCK=infinity LimitNOFILE=65535 #Type=simple # idle: similar to simple, the actual execution of the service binary is delayed # until all jobs are finished, which avoids mixing the status output with shell output of services. Type=idle RemainAfterExit=yes User=oracle Group=oinstall ExecStart=/home/oracle/scripts/start_all.sh ExecStop=/home/oracle/scripts/stop_all.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Thanks to Fr3dY in the comments for pointing out the NFS dependency management using
Requires and After and the issue with systemd and PAM limits.
Reload
systemd so it can see the new service.# systemctl daemon-reload
Start the service and enable so it is automatically restarted on reboot.
# systemctl start dbora.service # systemctl enable dbora.service ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/dbora.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/dbora.service' # systemctl status dbora.service dbora.service - The Oracle Database Service Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/dbora.service; linked) Active: active (exited) since Tue 2015-03-24 10:55:28 GMT; 5min ago Process: 6145 ExecStart=/home/oracle/scripts/start_all.sh (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 6145 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Mar 24 10:56:27 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: SQL> ORACLE instance started. Mar 24 10:56:27 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: Total System Global Area 1140850688 bytes Mar 24 10:56:27 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: Fixed Size 2923584 bytes Mar 24 10:56:27 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: Variable Size 419431360 bytes Mar 24 10:56:27 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: Database Buffers 704643072 bytes Mar 24 10:56:27 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: Redo Buffers 13852672 bytes Mar 24 10:56:31 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: Database mounted. Mar 24 10:56:33 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: Database opened. Mar 24 10:56:33 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: SQL> Disconnected from Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Re...ction Mar 24 10:56:33 ol7-121.localdomain startup.sh[6145]: With the Partitioning, OLAP, Advanced Analytics and Real Applica...tions Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full. #
Comments
Post a Comment